- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRONICS > 2017 > IEEE > DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
Illegally parked vehicles on the urban road may create a traffic flow problem as well as a potential traffic accident, such as crashing between parked and other vehicles. Thus, the intelligent traffic monitoring system should be able to prevent this situation by integrating an illegally parked vehicle detection module. However, implementing such a module becomes more challenging due to road environments, such as weather conditions, occlusion, and illumination changing. Hence, this work addresses a method to implement an illegally parked vehicle detection based on the cumulative dual foreground differences from the short and long-term background models, temporal analysis, vehicle detector, and tracking.
Adaptive Dual Background Model, Spatiotemporal Maps, Adaptive Gaussian Mixture Model.
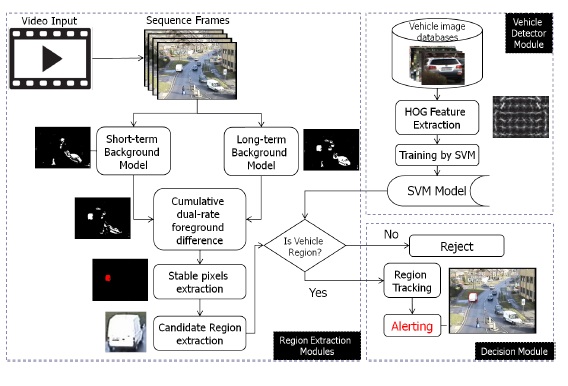
This work proposed cumulative dual foreground differences and temporal event analysis to detect illegally parked vehicles, as an important part of a vision-based intelligent traffic monitoring system. To decide an illegally parking event in the monitoring area, the detection based tracking is performed. Our framework is based on dual-rates background modeling and subtraction. Technically, the proposed method consists of four main stages: dual-rates background modeling, candidate static pixel extraction, stable region extraction, and tracking. First, short- and long-term background modeling was built for k consecutive frames within one period (e.g. one second), using two different learning rates. Static foreground pixels are then extracted separately from each model. The cumulative values of foreground differences in each pixel location are calculated within a time period. These values are used to determine the stability of the pixels and forming stable regions. Once candidate regions are extracted, the geometry filtering and vehicle detector are performed to reject false candidates. The duration of the vehicle being parked is counted using detection based tracking approach. Lastly, if the duration is more than a particular time, the alarm is triggered.
BLOCK DIAGRAM