- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRICAL > 2017 > IEEE > POWER ELECTRONICS
This paper begins by presenting a generalized methodology for conceptualizing modular multilevel converter (MMC)-based dc-dc topologies that is predicated on the concept of harmonic power balance. A compelling implication is that MMC-based variants of conventional switched-mode converter structures can be realized. As an example case study, this paper introduces a new dc-dc MMC for HVDC applications that is derived from the classical buck-boost dc-dc converter. This new topology, which is revealed to be an alternative option to the well-known dual active bridge (DAB) converter with intermediate transformer, offers buck-boost functionality and bidirectional dc fault blocking using only two-quadrant switching cells. Comparative analysis shows the proposed topology has lower operating losses and lower total magnetics rating in comparison to an MMC-based DAB solution for dc stepping ratios around unity. A dynamic controller is developed that regulates the converter dc power throughput while maintaining balanced capacitor voltages.
Modular Bidirectional Converter.
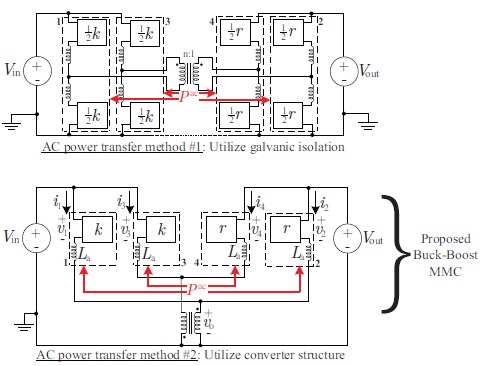
This paper proposes a new modular multilevel non-isolated dc-dc converter for MVDC and HVDC applications that provides buck-boost functionality and dc fault isolation using only half-bridge SMs. The proposed buck-boost MMC can also achieve up to a 92% reduction in installed magnetics rating relative to a traditional DAB solution for dc stepping ratios around unity. It will be shown that the proposed buck-boost MMC is an alternative option to the DAB approach for dc-dc conversion in MVDC and HVDC systems. Before introducing the proposed converter, the paper begins by formulating a generalized methodology to conceptualize MMC-based dc-dc topologies. Using the concept of harmonic power balance, it will be shown that MMC-based variants of any conventional switched-mode dc-dc converter structure (e.g., buck, buckboost, flyback, etc.) can be realized. It is hoped this will aid researchers in developing other new modular multilevel converter topologies suitable for MVDC and HVDC systems. The contribution of this paper is two-fold 1) The principle of harmonic power balance is exploited as the kernel of a generalized methodology for conceptualizing modular multilevel dc-dc converter topologies suitable for MVDC and HVDC applications; 2) The developed tool is used to derive a new modular multilevel dc-dc buck-boost converter from the classical switched-mode buck-boost architecture that has dc fault blocking capability. In general, the proposed topology can utilize an arbitrary number of interleaved phases.
MMC-Based Dc-Dc Buck Converter
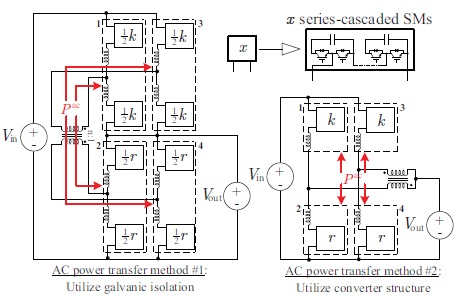
MMC-Based Dc-Dc Buck-Boost Converter