- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRICAL > 2017 > IEEE > POWER ELECTRONICS
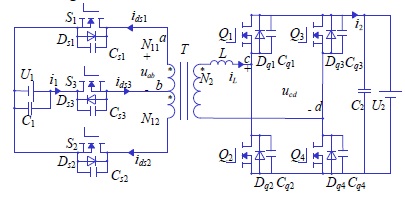
A novel zero-voltage-switching bidirectional dc/dc converter for energy storage system is proposed in this paper. The primary side is the improved push-pull topology adding one switch to achieve ZVS and the secondary side is full-bridge topology. Compared with the conventional DAB (Dual-active-bridge) dc/dc converter, the proposed converter applies a three-switch topology substituting for the full-bridge structure in the low voltage side of transformer with seven switches in all. With minimum switch, the cost of the driving circuit can also be saved and the stability of the whole system can be better guaranteed. Most of all, the proposed converter can realize the advantages of DAB, such as bidirectional power transmission and zero-voltage-switching (ZVS). Besides, it has no increase in power losses and transformer volume reaching relatively the same effect of the DAB.
Optimized Modulation Method.
In this paper, a new bidirectional converter is proposed in this paper, which is composed of a three-switch push-pull topology and a full-bridge topology. Theoretically, the three-switch push-pull topology can also be applied to the secondary side, and the working principle is the same. However, it has a non-negligible problem that the voltage stress of the three-switch topology is twice the input voltage, so it is not suitable for high voltage application. When the energy transfers between medium-to-low voltage and high voltage such as in battery energy storage system where the DAB topology also be applied, the proposed topology has the same effect with the DAB. Due to the switching sequence of the three-switch push-pull converter, the primary side can directly produce a high frequency voltage with the three-level wave instead of the two-level wave to reduce the reactive power, which serves as the function of the inner phase-shift angle of one active bridge to achieve the same effect of EPS control. Other control methods applied in the DAB except SPS control can also be used here to achieve the same effects. Besides, reducing the number of the power switch not only means saving the cost of the switch, but can also means less switching loss, reducing the number of the driving circuit and the cost and increase the stability of the converter. Most importantly, the proposed converter can reach the similar characteristic of the DAB without increasing power loss and transformer volume.
The proposed minimum switch zero-voltage-switching bidirectional dc/dc converter