- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRICAL > 2017 > IEEE > POWER ELECTRONICS
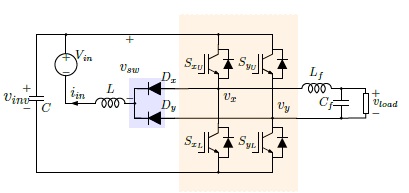
This paper investigates and evaluates the performance of a single-phase split-source inverter (SSI), where an alternative unidirectional dc-ac configuration is used. Such configuration is utilized in order to use two common-cathode diodes in a single-device instead of using two separate diodes, resulting in minimum parasitic inductance in the commutation paths. In this paper, the analysis and modulation of the single-phase SSI using this alternative configuration is discussed, and the analysis of the low frequency component in the dc side is introduced. Moreover, the features behind employing the triangular, the trailing-edge sawtooth, and the leading-edge sawtooth carriers with the single-phase SSI are discussed, and the differences among these carriers are highlighted. In order to highlight the performance of the proposed SSI, a comparative study is conducted with the two-stage architecture and the single-phase quasi-Z-source inverter (qZSI).
Modulation
This paper studies and evaluates the performance of the single-phase SSI, including a dc side low frequency component analysis. In this study, the single-phase SSI modulation using the triangular, the trailing-edge sawtooth, and the leading-edge sawtooth carriers is discussed, and their features are highlighted. Furthermore, the single-phase SSI is compared with the two-stage architecture using a BC-fed single-phase full-bridge VSI and the quasi-Z-source inverter (qZSI). The single-phase operation of the split-source inverters (SSIs), considering the unidirectional dc-ac operation, has been studied in this paper and an alternative configuration has been utilized, in which it is possible to use a common-cathode dual-diode package instead of two separate diodes to minimize the parasitic inductance in the commutation path of these diodes. Moreover, the high frequency commutation problem of these input diodes has been investigated and different carriers have been studied. Among the triangular, the trailing-edge sawtooth, and the leading-edge sawtooth carriers, the latter achieves one commutation of the input diodes at the lowest possible current value, which equals half of the minimum input current. Meanwhile, to maintain similar differential output voltage and use similar output filter, the switching frequency of the sawtooth carriers should be doubled, resulting in having the same number of high frequency commutations of the input diodes as the triangular one, increased number of bridge commutations, and reduced input inductance. Furthermore, using the leading-edge sawtooth carrier, it is possible to obtain zero commutating current of these input diodes in the discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) of the inductor current.
An alternative configuration of the single-phase split-source inverter (SSI)