- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRICAL > 2017 > IEEE > POWER ELECTRONICS
Modular Multilevel Converter (MMC) based Multi-terminal HVDC (MTDC) transmission is a favorable option for asynchronously interconnecting several weak ac systems. This paper investigates the potential resonance of such a MMC-MTDC system excited by background harmonics in any of the MMC’s ac systems and the undesirable transfer of these harmonics to the remote ac systems. First, the harmonic transfer rule across one MMC is established using phase leg voltage analysis and it is then used to develop an equivalent circuit model of the MMC-MTDC system. This model is used to investigate the mechanism of resonance excited by ac side background harmonics. Finally, a control strategy is proposed to mitigate this resonance.
Frequency Scanning Method
In a multi-terminal HVDC system with MMC converters, the ac background harmonics in one converter’s ac network may transfer through the dc transmission system to the ac systems of the other converters. It is shown that the problem is particularly severe when the dc side is resonant at the complementary frequencies of the ac side background harmonics. The mechanism for the harmonic transfer from the ac system to the MMC’s phase legs is analyzed to understand how the ac background harmonics transfer to dc network and other ac systems. Based on this analysis, a simple equivalent model of the converter viewed from the dc side is developed, which considers the converter as a harmonic source behind a reactance. This model is sufficient to determine the resonant frequencies of the dc side. A control strategy to eliminate the resonance caused by ac background harmonics is proposed. This is achieved by generating a counteracting zero sequence phase leg voltage order that eliminates the zero sequence current at the problem harmonic frequencies. This control strategy can successfully isolate the dc side from the ac side harmonics of the MMCMTDC system and prevent their further transfer to the ac systems of the other converters. Furthermore, it only uses local signals, rendering communication to and from the remote converters unnecessary.
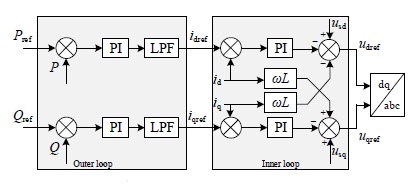
MMC Controller