- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRONICS > 2020 > IEEE > DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
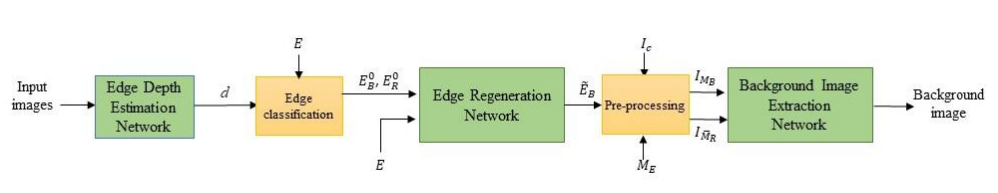
When imaging through a semi-reflective medium such as glass, the reflection of another scene can often be found in the captured images. It degrades the quality of the images and affects their subsequent analyses. In this paper, a novel deep neural network approach for solving the reflection problem in imaging is presented. Traditional reflection removal methods not only require long computation time for solving different optimization functions, their performance is also not guaranteed. As array cameras are readily available in nowadays imaging devices, we first suggest in this paper a multiple-image based depth estimation method using a convolutional neural network (CNN). The proposed network avoids the depth ambiguity problem due to the reflection in the image, and directly estimates the depths along the image edges. They are then used to classify the edges as belonging to the background or reflection. Since edges having similar depth values are error prone in the classification, they are removed from the reflection removal process. We suggest a generative adversarial network (GAN) to regenerate the removed background edges. Finally, the estimated background edge map is fed to another auto-encoder network to assist the extraction of the background from the original image.
Wasserstein generative adversarial network (WGAN), blind image separation (BIS)
In this paper, a new multiple-image based reflection removal algorithm using deep neural networks is proposed. This paper proposes a novel deep learning based algorithm to solve the ill-posed reflection removal problem. This approach has no pre-requisites as in the previous approaches on the property of the reflection image. It also does not have the restrictions as in the previous approaches due to the use of different motion models and the need of accurate initialization of the parameters. For images with reflection, their depth is known to be ambiguous in general. It develops a new CNN approach that directly estimate from the multiple-image input the depth values along the image edges. Due to the edge independence property, we can classify many of the edge pixels as belonging to the background or reflection without ambiguity. Since the edges in the shared depth region are error prone, we regenerate these edges by using a WGAN. Thus, it converts the original reflection removal problem to be an edge regeneration problem. We also show that an image with reflection has a significant difference in its statistical distribution from that of normal images. A WGAN can learn through the massive training process to generate the required data that follow the distribution of normal images. Instead of using the traditional time-consuming optimization process, we use another auto-encoder to extract the background image from the original one based on the estimated background edges. High level features are adopted in the training of the auto-encoder and the input is also pre-processed to remove the strong edges of reflection. They both contribute to the improved performance of the proposed algorithm. Since DNN techniques are adopted in all components of the proposed algorithm, a significant improvement in the computation speed is achieved as compared to the traditional optimization approaches.
BLOCK DIAGRAM