- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRONICS > 2020 > IEEE > DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
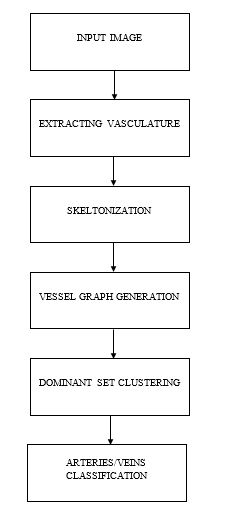
The estimation of vascular network topology in complex networks is important in understanding the relationship between vascular changes and a wide spectrum of diseases. Automatic classification of the retinal vascular trees into arteries and veins is of direct assistance to the ophthalmologist in terms of diagnosis and treatment of eye disease. However, it is challenging due to their projective ambiguity and subtle changes in appearance, contrast and geometry in the imaging process. In this paper, we propose a novel method that is capable of making the artery/vein (A/V) distinction in retinal color fundus images based on vascular network topological properties. To this end, we adapt the concept of dominant set clustering and formalize the retinal blood vessel topology estimation and the A/V classification as a pairwise clustering problem. The graph is constructed through image segmentation, skeletonization and identification of significant nodes. The edge weight is defined as the inverse Euclidean distance between its two end points in the feature space of intensity, orientation, curvature, diameter, and entropy. The reconstructed vascular network is classified into arteries and veins based on their intensity and morphology. The proposed approach has been applied to five public databases, INSPIRE, IOSTAR, VICAVR, DRIVE and WIDE, and achieved high accuracies of 95.1%, 94.2%, 93.8%, 91.1%, and 91.0%, respectively. Furthermore, we have made manual annotations of the blood vessel topologies for INSPIRE, IOSTAR, VICAVR, and DRIVE datasets, and these annotations are released for public access so as to facilitate researchers in the community.
k-Nearest Neighbour (kNN) classifier
The concept of dominant set clustering has been introduced to tackle the challenging problem of vasculature analysis, and proved to be an effective way of addressing the problem of tracing crossovers. The proposed method can split the entire blood vessel graph into several individual branches as subtrees, and is capable of demonstrating how different blood vessels are anatomically connected to each other. In addition, the A/V classification is undertaken on the topology-assigned blood vessel network, rather than the entire blood vessel segments. The proposed method has been validated quantitatively using five publicly accessible datasets, with promising results. In addition, the manual annotations of blood vessel topologies of four datasets were established as the ground truth, and have been released for public access.
BLOCK DIAGRAM