- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRONICS > 2017 > IEEE > DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
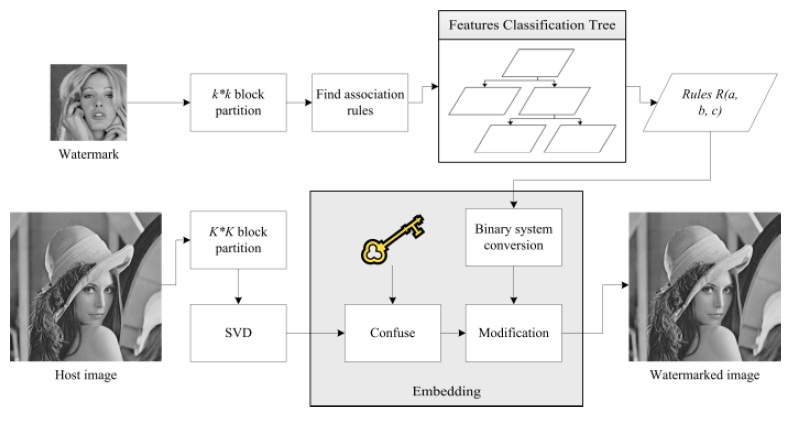
A novel watermarking scheme is proposed that could substantially improve current watermarking techniques. This scheme exploits the features of micro images of watermarks to build association rules and embeds the rules into a host image instead of the bit stream of the watermark, which is commonly used in digital watermarking. Next, similar micro images with the same rules are collected or even created from the host image to simulate an extracted watermark. This method, called the Features Classification Forest, can achieve blind extraction and is adaptable to any watermarking scheme using a quantization-based mechanism. Furthermore, a larger size watermark can be accepted without an adverse effect on the imperceptibility of the host image.
Contourlet Transform, Wavelet Transform, Histogram Intersection Technique.
In this paper, several discussions are proposed to cover the whole concept of the Features Classification Forest. In the beginning, the tradeoff among the three criteria, the imperceptibility, robustness, and capacity, is presented to explain the main topic of digital watermarking techniques. To make advancement beyond the current limitations, the idea of using micro images inside the host image to simulate a watermark is inspired from association rules and consequently facilitates the creation of the Features Classification Forest. Before constructing the model, the image analysis section clearly introduces the similarity and disparity of blocks of different images based on three features – the contrast, average pixel value, and angle. The evidence of similarity underpins the basis of the classification, and the disparity develops the different types of tree structures. After the model of the Features Classification Forest is established, the next step is to validate the assumption – once the blocks from the different images follow the same association rules, the textures of the blocks would be similar. In other words, by means of the FCT, the watermark can be reassembled by using similar blocks from the host image. In addition, the adaptive SVD-based scheme and the other four schemes are used for proving the applicability and showing the intrinsic characteristics within each scheme.
BLOCK DIAGRAM