- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRICAL > 2017 > IEEE > POWER ELECTRONICS
An impedance networks DC-DC boost converter is developed in this paper. Compared to the conventional boost converter it can reach a higher voltage gain with fewer diodes and a small duty cycle (smaller than 33%), meanwhile avoid instability caused by saturation of its inductors, whereas the conventional boost converters realize high voltage gains at rather large duty cycles (normally exceeding 50%) resulting in saturation of inductors. Further, it can well fulfill the stringent industrial requirements, particularly of renewable power systems. The proposed converter with continuous conduction modes is analyzed for different states of its components. Then, it is shown how to determine its various parameters.
Step-Up Dc-Dc Converter, Interleaved Forward-Flyback Boost Converter.
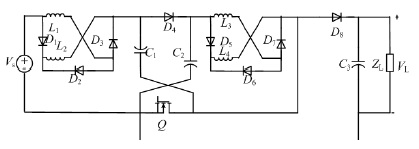
High-step-up and high-efficiency DC-DC converters are necessary to handle large input currents and to reach high output voltages, e.g. where the low voltages of renewable energy sources need to be boosted to high voltages for feeding into grid-connected inverters. Theoretically, conventional boost converters may realize infinite voltage gains for switching duty-cycles very close to 100% which, however, degrade the converters’ overall efficiency. This drawback is overcome by the proposed high-step-up boost converter. Compared to the traditional boost converters, the proposed one reaches a higher voltage gain with fewer diodes, and with a small duty-cycle to avoid inductor saturation. Its design combines three active cross-shaped networks, viz. a boost part at the input consisting of two inductors and three diodes, a switching part consisting of a switch, two capacitors and a diode, and a boost part at the output consisting of two inductors and three diodes. By suitably adjusting the duty-cycle, desired voltage gain in renewable energy systems can be achieved. To overcome the drawbacks and challenges outlined above, a novel impedance networks boost converter with high-voltage gain is proposed, which can be used to boost the output voltages of renewable-energy systems. It does not only realize a higher voltage gain with a small duty cycle to prevent saturation of inductors, but also uses fewer components.
The proposed DC-DC boost converter