- ALL COMPUTER, ELECTRONICS AND MECHANICAL COURSES AVAILABLE…. PROJECT GUIDANCE SINCE 2004. FOR FURTHER DETAILS CALL 9443117328


Projects > ELECTRICAL > 2017 > IEEE > POWER SYSTEMS
Although the future impact of Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEV) on distribution grids is disputed, all parties agree that mass operation of PEVs will greatly affect load profiles and grid assets. The large-scale penetration of domestic energy storage, such as with Photovoltaics (PVs), into the edges of LV grids is increasing the amount of customer-generated electricity. Distribution grids, which are inherently unbalanced, tend to become even more so with the uneven spread of PVs and PEVs. In combination, PEVs and local generation could provide voltage support for distribution networks, and support increased penetration. This paper develops an interactive energy management system (EMS) for incorporating PEVs in demand response (DR). Using this system, owners can immediately choose whether they want to discharge their PEV battery back into the grid. The system not only provides owners with a flexible scheme for contributing to DR but also ensures that, through real-time collaboration of PEVs and PVs, the 3-phase grid operates within acceptable voltage unbalance.
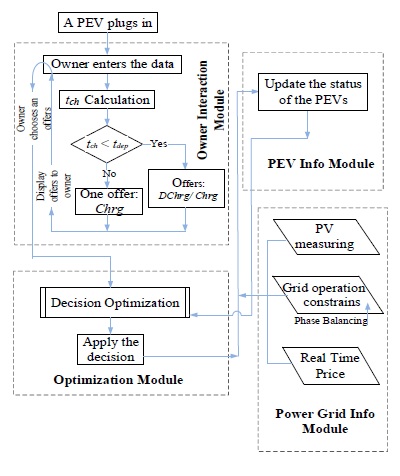
Real-Time Energy Management Algorithm.
The present study has proposed an interactively structured EMS that includes single or small garages distributed over a 3-phase LV system. This structure offers PEV owners a flexible scheme for contributing to DR while avoiding the inconvenience and limitations of long-term contracts. The aggregator offers various options based on the comfort criterion factor, and vehicle owners respond based on preference. Five different modules are offered for the decision-making process. The proposed method also ensures that the existing 3-phase infrastructure distribution grid operates within acceptable voltage unbalance limits. To provide clarification of the unbalance condition, solar/PV units have also been included in the analysis. The first step in this EMS was an analysis of the voltage unbalance impact of charging under low and high PEV penetration. PEVs and solar units were then employed in combination for phase-unbalance mitigation.
Structure of the proposed decision optimization module
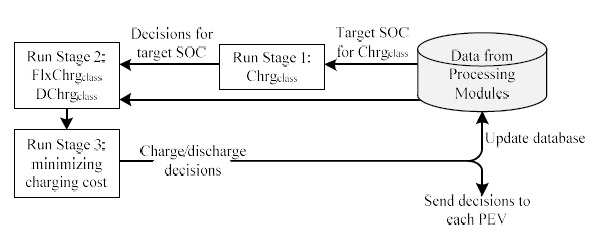
The structure of the decision making algorithm